Is Biomass Pellets from Bio Waste Manufacturing Profitable?

In the quest for sustainable and renewable energy sources, biomass pellets made from bio waste have emerged as a promising solution. These pellets, derived from organic waste materials, offer an eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels, contributing to energy security and environmental conservation. However, the profitability of manufacturing biomass pellets from bio waste hinges on several factors, including raw material availability, production costs, market demand, and regulatory support. This article delves into the economic viability of biomass pellet manufacturing, examining the factors that influence profitability and the potential benefits of this green industry.
Understanding Biomass Pellets
What are Biomass Pellets?
Biomass pellets are cylindrical fuel rods made from compressed organic materials. These materials typically include agricultural residues (such as straw and husks), forestry by-products (like sawdust and wood chips), and industrial bio waste (including paper mill residues and food processing waste). The pellets are produced by drying and grinding the raw materials into a fine powder, which is then compressed under high pressure to form dense, uniform pellets.
Benefits of Biomass Pellets
The primary advantages of biomass pellets include their renewable nature, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and high energy efficiency. When burned, biomass pellets release carbon dioxide that is roughly equivalent to the amount absorbed by the plants during their growth, making them a carbon-neutral energy source. Additionally, their high energy density and uniform shape make them easy to store, transport, and handle, enhancing their appeal as a sustainable fuel alternative.
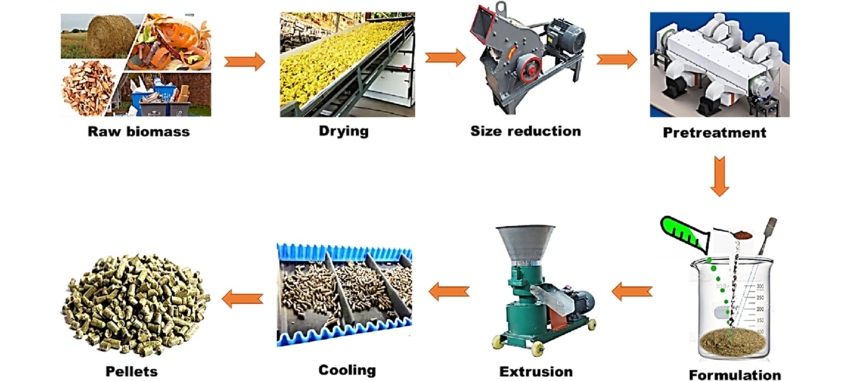
Factors Influencing Profitability
Raw Material Availability and Cost
The profitability of biomass pellet manufacturing largely depends on the availability and cost of raw materials. Regions with abundant agricultural and forestry activities often have a steady supply of bio waste, which can be procured at a low cost or even for free in some cases. For example, countries with extensive agricultural production, like India and Brazil, generate significant amounts of crop residues that can be used for pellet production. The cost of collecting, transporting, and processing these materials, however, must be factored into the overall production costs.
Production Technology and Efficiency
Advancements in pellet production technology have made the process more efficient and cost-effective. Modern pellet mills are capable of processing various types of bio waste with minimal energy consumption and high output rates. The initial investment in machinery and equipment can be substantial, but the long-term benefits of improved efficiency and reduced operating costs can enhance profitability. Additionally, economies of scale play a crucial role, as larger production volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs.
Market Demand and Price
The demand for biomass pellets is driven by several factors, including energy prices, environmental regulations, and consumer preferences for sustainable products. In regions with high energy costs or stringent emission standards, biomass pellets can offer a competitive and eco-friendly alternative to traditional fuels. Government incentives and subsidies for renewable energy projects can also boost demand and support higher market prices for biomass pellets. The global market for biomass pellets has been growing steadily, with significant demand in Europe, North America, and Asia.
Regulatory and Policy Support
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the biomass pellet industry. Supportive policies, such as subsidies for renewable energy, tax incentives, and grants for bioenergy projects, can significantly enhance the profitability of biomass pellet manufacturing. Conversely, stringent regulations on emissions and waste disposal can increase operational costs but also drive demand for cleaner energy solutions like biomass pellets. It is essential for manufacturers to stay informed about regulatory developments and leverage available support mechanisms.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Lessons Learned
European Union
The European Union (EU) has been at the forefront of promoting biomass energy, with several member countries implementing policies to support the biomass pellet industry. For instance, Sweden has successfully integrated biomass pellets into its energy mix, reducing its reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions. Government incentives, such as feed-in tariffs and renewable energy certificates, have played a crucial role in fostering the growth of the biomass pellet market. The Swedish experience highlights the importance of policy support and market incentives in driving the profitability of biomass pellet manufacturing.
United States
In the United States, the biomass pellet industry has also seen significant growth, particularly in states with abundant forestry resources like Maine and Oregon. The production of wood pellets for export to European markets has become a lucrative business, driven by the demand for renewable energy in the EU. American manufacturers have benefited from economies of scale and technological advancements, which have reduced production costs and improved pellet quality. The success of the U.S. biomass pellet industry underscores the potential for profitability through market diversification and technological innovation.
India
India presents a unique case, with its vast agricultural sector generating substantial amounts of bio waste. Initiatives like the National Biomass Policy and various state-level programs have encouraged the use of biomass for energy production. Small-scale biomass pellet manufacturing units have sprung up in rural areas, providing an additional income stream for farmers and reducing agricultural waste. The Indian experience demonstrates the potential for integrating biomass pellet production with agricultural activities, creating a sustainable and profitable business model.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Supply Chain Management
One of the significant challenges in biomass pellet manufacturing is managing the supply chain efficiently. Ensuring a consistent and reliable supply of raw materials requires effective coordination with suppliers, transportation logistics, and storage facilities. Establishing long-term contracts with farmers, forestry operators, and industrial producers can help secure a steady supply of bio waste. Investing in infrastructure, such as storage silos and efficient transport systems, can also mitigate supply chain disruptions.
Quality Control
Maintaining consistent pellet quality is crucial for market acceptance and profitability. Variations in raw material composition and processing conditions can affect the calorific value, moisture content, and ash content of the pellets. Implementing stringent quality control measures, such as regular testing and adherence to industry standards, can ensure that the final product meets customer expectations. Advanced monitoring and control systems can help optimize the production process and minimize quality variations.
Environmental Impact
While biomass pellets are considered a green energy source, their production and use can have environmental implications. Harvesting raw materials, especially from forestry operations, must be done sustainably to prevent deforestation and habitat destruction. Additionally, the emissions from pellet combustion, although lower than fossil fuels, must be managed to minimize air pollution. Adopting best practices in sustainable sourcing, production, and combustion can enhance the environmental benefits of biomass pellets.
Future Prospects and Opportunities
Technological Innovations
Continuous advancements in technology offer exciting opportunities for the biomass pellet industry. Innovations in pellet production, such as torrefaction and steam explosion, can enhance pellet quality and energy efficiency. Research into new feedstocks, such as algae and other non-food biomass, can diversify raw material sources and reduce competition with food production. The integration of digital technologies, such as IoT and blockchain, can improve supply chain transparency and operational efficiency.
Market Expansion
The global demand for renewable energy is expected to grow, driven by increasing energy consumption, environmental concerns, and policy support. Emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and Latin America present significant opportunities for biomass pellet manufacturers. Developing partnerships and distribution networks in these regions can help tap into new markets and enhance profitability. Additionally, expanding product offerings, such as customized pellets for specific applications, can cater to niche markets and increase market share.
Policy Support
Governments around the world are likely to continue promoting renewable energy and sustainable practices through various policy measures. Engaging with policymakers and industry associations can help shape favorable regulatory environments and secure support for biomass pellet projects. Advocacy efforts, such as highlighting the environmental and economic benefits of biomass pellets, can garner public and political backing for the industry.
Conclusion
The profitability of biomass pellet manufacturing from bio waste is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including raw material availability, production efficiency, market demand, and regulatory support. While challenges exist, the potential benefits in terms of environmental sustainability, energy security, and economic opportunities make it a compelling industry. Success stories from around the world demonstrate that with the right strategies and support, biomass pellet manufacturing can be a profitable and sustainable business. As the global push for renewable energy intensifies, the biomass pellet industry is poised for significant growth, offering a viable pathway to a greener future.










